Everything You’ve Wanted To Know About EV Charging

At Cartelligent, we’ve seen firsthand the surging interest in electric vehicles. Many of our clients are making the shift to EVs, and with that comes a common question: “How does EV charging actually work?” Understanding how to power your electric vehicle is key to a seamless EV ownership experience. This guide will demystify the 3 EV charging levels, ensuring you feel confident whether you’re at home or on the go, and help you decide if you want to buy or lease an EV.
What We’ll Cover:
- AC vs. DC: Understanding the Core of EV Charging
- Level 1 Charging
- Level 2 Charging
- Level 3 (DC Fast) Charging
- Cutting the Cord: How Wireless EV Charging Works
- Tesla Superchargers: Expanding Compatibility for All EVs
- How to Easily Find Charging Stations Near You
- Free Charging: Which EVs Offer Complimentary Power?
AC vs. DC: Understanding the Core of EV Charging
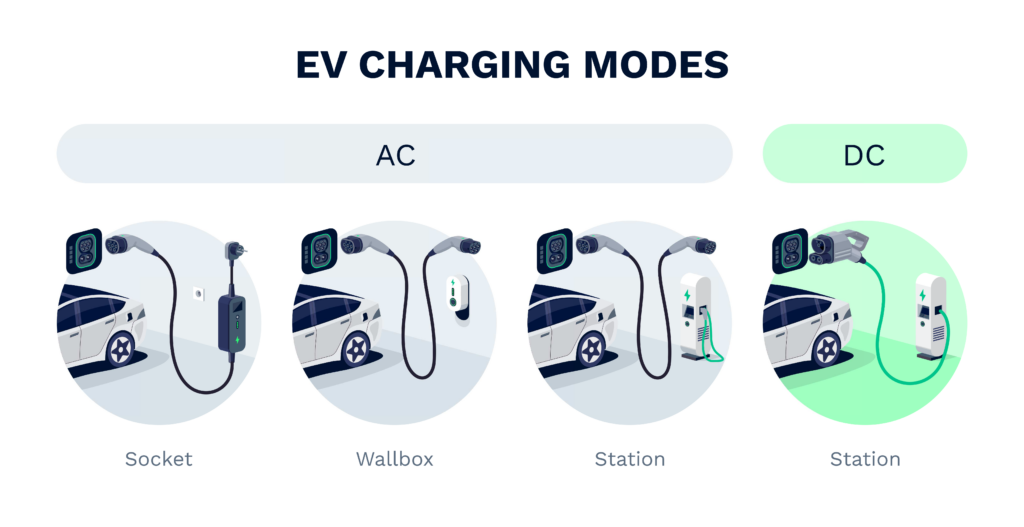
When exploring EV charging options, you’ll often hear the terms AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current). AC is the electricity you use daily from wall outlets. This type of charging is similar to plugging your phone into a computer’s USB port; the computer (AC) supplies electricity, but the phone must convert AC to DC for battery charging. Since AC must be converted to DC by your vehicle’s on-board charger, AC charging is slower than direct current (DC) charging. DC, on the other hand, delivers electricity directly to the battery, making it significantly faster because no conversion time is needed.
Level 1 (AC) Charging: Simple and Convenient
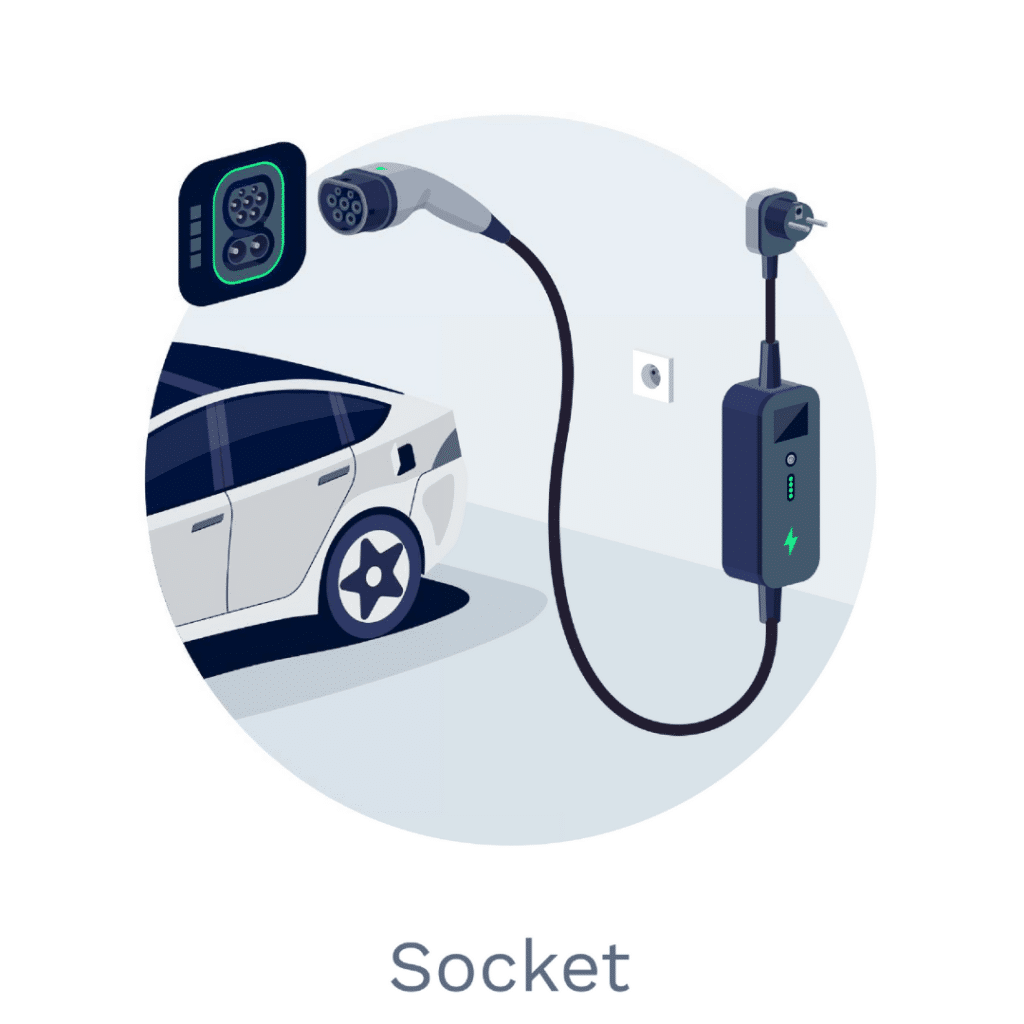
Level 1 charging for EVs offers between 1.4 kW to 2 kW of power. It’s the most convenient and requires no extra installation; simply plug directly into a standard wall outlet. This charging level is a good interim solution for first-time EV owners planning on upgrading to a Level 2 charger, those with short commutes, or for charging in off-street parking where you can plug in overnight like you would your phone, waking up to a ready-to-go vehicle for short commutes.
Level 2 (AC) Charging: The Everyday Solution
Level 2 Charging is commonly installed in private homes, workplaces, and public infrastructure. Offering between 6 kW to 19.2 kW of power, it’s ideal for overnight charging at home or during longer stops at public charging stations, like catching a movie or grabbing groceries.
- Cost: $500-$2,000 depending on if a basic set-up or complex installation is required
- Charging time for PHEV: 1-2 hours*
- Charging time for EV: 4-10 hours*
- Use cases: public charging and overnight at home
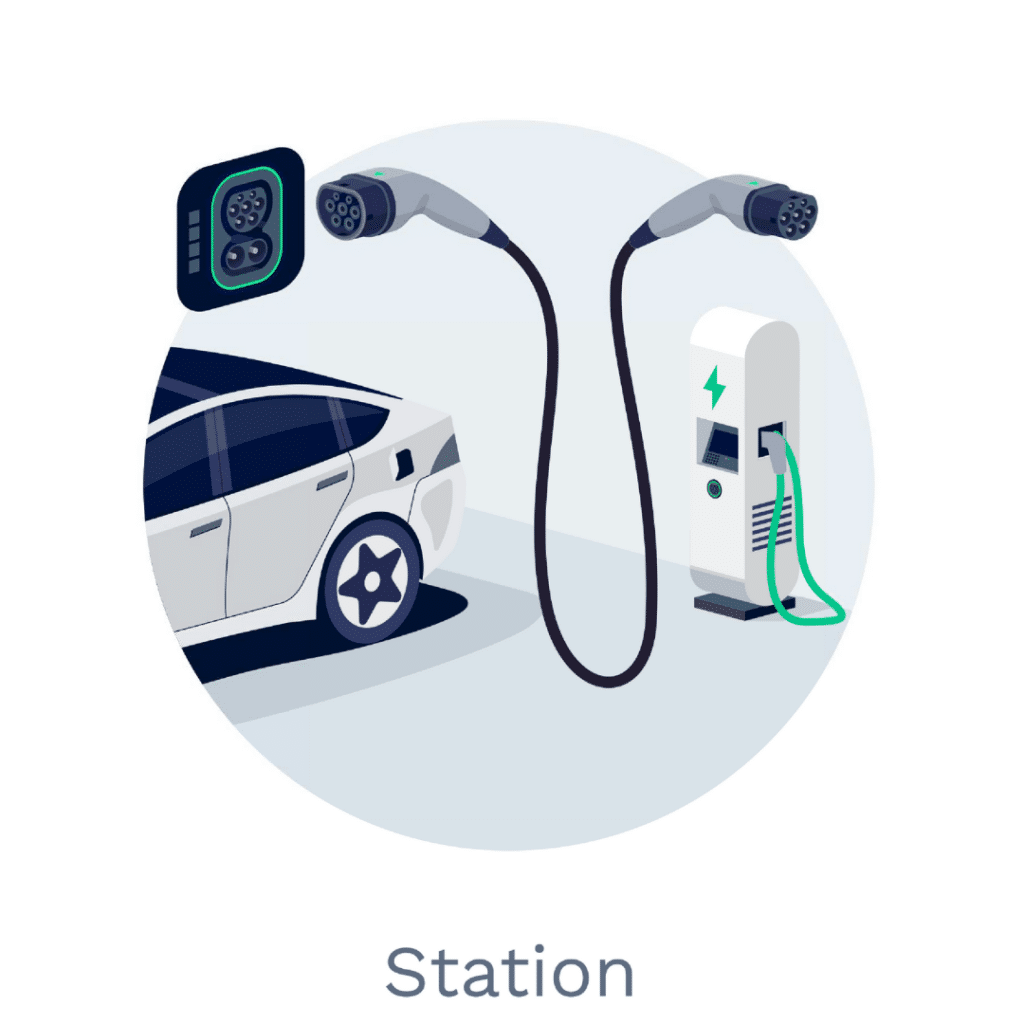
Level 3 (DC Fast) Charging: Powering Up Quickly
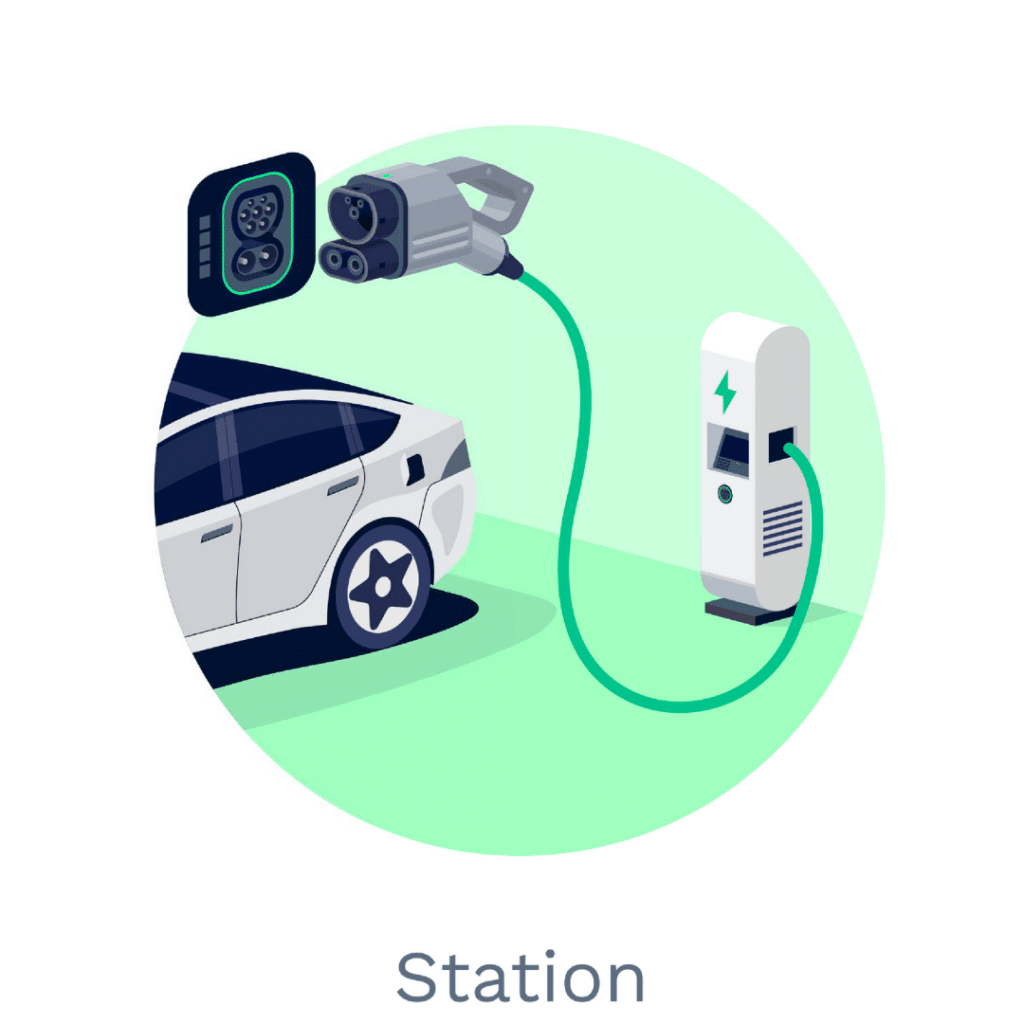
Level 3 charging, also known as DC Fast Charging, is the fastest charging type currently available. With a power output ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, it rapidly supplies direct current (DC) straight to the battery.
- Charging time for PHEV: N/A
- Charging time for EV: Around 20-1 hour*
- Use cases: Public charging
Tesla Superchargers fall into this category.
*All charging times listed are estimated averages, actual time will vary based on engine size, vehicle age, temperature, and additional factors.
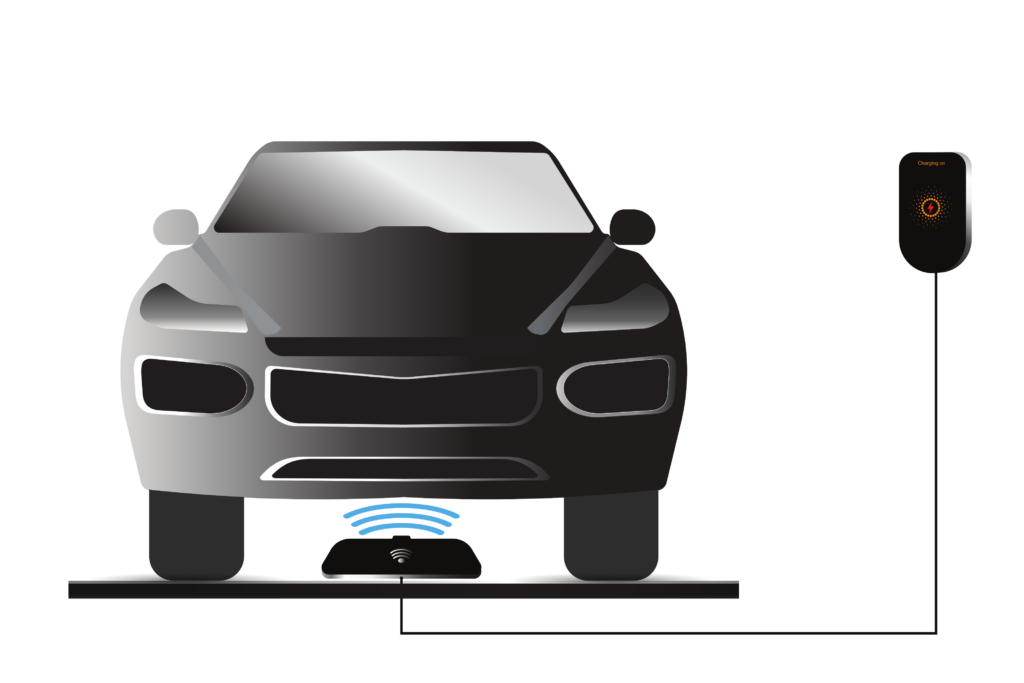
Cutting the Cord: How Wireless EV Charging Works
Imagine an EV charging experience free from cables. That future is closer than you think. Major companies have started building wireless charging prototypes for EVs, operating similarly to how wireless phone charging works. A conduit runs from a power box to a charging pad on the floor. When an EV parks over the pad, energy flows through a magnetic field, enabling wireless power transfer between the pad and vehicle receiver.
Unlike phone charging, you’d have more freedom with positioning, as wireless EV charging can safely transfer power over a larger area. According to WiTricity, a leader in wireless charging technology, engineers are actively working to integrate their systems with OEMs, aiming to make alignment seamless for drivers, potentially even by triggering front-facing cameras for guidance. However, for current EV owners, adding this technology may require a significant retrofit.
Given the rapid advancements in EV technology, including innovations like wireless charging, many drivers find that leasing a car offers unparalleled flexibility. An EV lease allows you to enjoy the latest features without long-term commitment. To explore if leasing is the right fit for your lifestyle, understanding federal tax credits and EV leasing loopholes is essential.
Tesla Superchargers: Expanding Compatibility for All EVs
As of now, there are three types of Tesla Superchargers: Tesla-only Superchargers, “All EVs” Superchargers using a Magic Dock adapter, or NACS (North American Charging Standard) Superchargers. As early as Q4 2024, select electric cars, like Ford’s 2025 Mustang Mach-E and 2025 F-150 Lightning, will be equipped with NACS charge ports.
Want to know when NACS-equipped new cars hit the market? Join over 30,000 subscribers who use Cartelligent’s newsletter to stay up to date on all things automotive. Simply scroll down to the bottom of this page to sign up.
Other automakers joining the list to access Tesla Superchargers include Audi, BMW, Cadillac, Chevrolet, Fiat, Ford, GMC, Honda, Hyundai, Jaguar, Kia, Lexus, Lucid, Mercedes, Mini Cooper, Nissan, Polestar, Porsche, Rivian, Rolls Royce, Subaru, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Volvo. While most automakers are currently experiencing delays due to Tesla organizational changes, software compatibility, and supply chain issues, the widespread adoption of NACS (North American Charging Standard) promises more streamlined payment and access in the future.
How to easily find charging stations near you
California boasts over 100,000 public or shared private electric vehicle chargers. With a $1.9 billion plan to build a more robust charging network, Californians can expect to see even more stations in the coming years. Apps like PlugShare, ChargeHub, and manufacturers’ proprietary apps offer an easy way to locate EV charging stations near you.
What electric vehicles have free charging?
Some electric vehicles offer complimentary charging programs, often through partnerships with specific charging networks like Electrify America. See the full list of vehicles that come with free charging here.
Get Answers to the Top EV Questions Straight to your Inbox
Still have questions about making the switch to an EV, or ready to find the best way to buy a car? We’re here to help. As expert advisors to new car shoppers, we at Cartelligent hear a lot of questions from potential EV owners. Get expert answers to your top EV questions, delivered right to your inbox, with our free email series. You’ll discover:
🔌 If an EV fits your current lifestyle
🔌 EV range and how to charge during trips
🔌 EV maintenance
🔌 How EV rebates work
🔌 How popular makes & models compare
🔌 The easiest way to get a new EV
Don’t navigate the EV landscape alone. Start your new car search today and let our car buying service guide you to your perfect electric vehicle! If you’re also considering how to sell your car or trade in your car as part of your EV transition, our auto broker team is ready to assist. For personalized guidance, schedule a free consultation with a Cartelligent expert advisor today.




